Hawaiian culture relates to traditions and a diverse art scene, and the elementary needs of those interested in parties remain unmet. Hawaiian-themed parties are growing more popular due to their vivid and exotic appearance. This trend should benefit the hawaiian party supply providers by purchasing large quantities of authentic supplies for hawaiian party that can be resold to consumers who appreciate both the tradition and glamour of Hawaiian-themed events.
Why People Want Supplies for Hawaiian Party
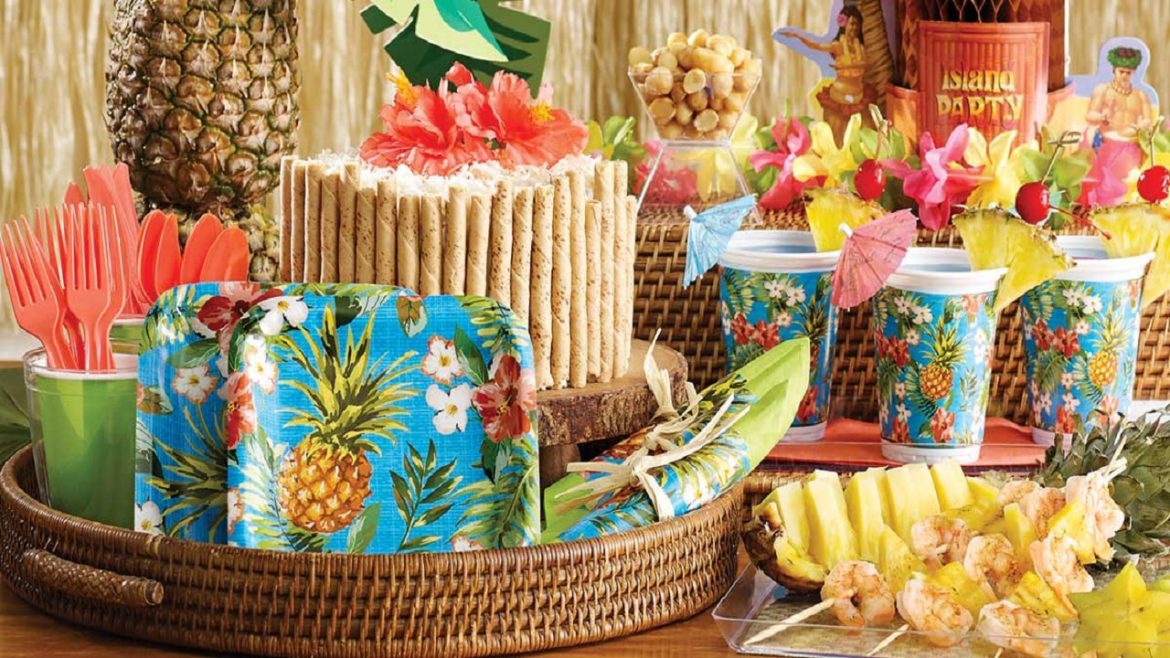
Hawaiian parties reflect the popular tradition associated with the Hawaiian culture. Weddings, birthdays, and business parties are social events, and the definite setting needs the correct decor. In this case, supplies for hawaiian party, such as floral leis, headbands, and tropical centerpieces, could not be missing. Leis made of fresh or synthetic flowers are always a part of every traditional Hawaiian affair, as are curly headbands, which add elegance and Polynesian taste to any ceremony. Similarly, floral and fruit centerpieces with palm fronds, hibiscus, and tropical fruits place an event-style Hawaii scene on each table. Serving an audience interested in supplies for hawaiian party also requires understanding their tastes. Such people may need quality, appropriate decorations showing the culture other than everyday plain or ordinary party essentials. Such products can only be provided by entrepreneurs capable of meeting the demands within this specific category with high frequency by buying them in bulk from wholesale suppliers like those on Alibaba.com.
Advantages of Ordering Supplies for Hawaiian Party
The following are the benefits businesses get when buying supplies for hawaiian party wholesale. First, merchants’ large purchases result in price reductions, which raise their profit margins. Suppliers may provide consumers significant discounts when purchase orders are placed in larger volumes, and business owners can sell their goods at competitive rates while still making enticing profits. Secondly, bulk sourcing helps avoid regular and frequent ordering of items in high demand. Decorative flowers such as leis and headbands are examples of classics that customers always look for. Stocking these items makes the business easily accessible to its loyal clientele and will be considered a stable supplier. Lastly, it is easier to make bulk purchases and manage the stock. Instead of processing several small orders that are inconsequential in volume, the business can better manage storage for optimal functionality. This efficiency is especially felt on occasions such as proms and Christmas or when people may rush to get Hawaiian-themed supplies.
Helping People Searching for Supplies for Hawaiian Party
Businesses must be more customer-oriented to appeal to the customer niche interested in supplies for hawaiian party. Due to intense competition, a company can develop and offer options like floral leis with specific names, orders, or themed centerpiece sets. Also, cultural identity in promoting products will attract customers desiring the oriental touch associated with Hawaii. This audience can be reached through e-commerce sites and social media. Therefore, detailed product descriptions, quality images, and creative content explaining Hawaiian traditions can help boost sales of the available products online. Greater cooperation with event planners and cultural institutions can only be a plus in enlarging the customer pool.
Conclusion
If the goal is to increase sales of supplies for hawaiian party, then quality, authenticity with customers, and fulfilling the current demand are the keys for businesses. This niche is characterized by low consumption by each customer. Hence, volume purchasing is appropriate for the market segmentation strategy.